
Lead Image © Mellimage, 123RF.com
Citrix NetScaler steps in for Microsoft TMG/ISA
Into the Breach
NetScaler is a network product that works as an application accelerator and firewall. In other words, integration of the product into the enterprise is best handled by networking experts, because that's where network traffic is directly influenced and controlled. The complexity of NetScaler far exceeds the requirements for managing Citrix products like XenDesktop or XenApp, so you should not underestimate the product despite its apparent simplicity.
Citrix claims that its NetScaler products are the best replacement for Microsoft TMG. The manufacturer has published a corresponding white paper [1] to support this claim. The main advantages of TMG were the built-in wizards that helped admins provide Exchange services, SharePoint, and Lync efficiently on the Internet. Citrix fills the void created by the withdrawal of TMG with its NetScaler products, which are said to offer the full feature set of TMG. NetScaler also has integrated wizards and templates to keep the configuration as simple as possible (Figure 1). However, that's not all.
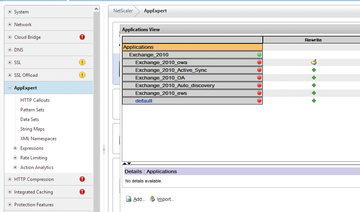 Figure 1: Citrix NetScaler uses wizards to help you provide Exchange, SharePoint, and Lync on the web.
Figure 1: Citrix NetScaler uses wizards to help you provide Exchange, SharePoint, and Lync on the web.



