« Previous 1 2 3 Next »
Secure and seamless server access
Lightning
Typically, developers invest considerable time and effort to secure their Internet property with methods such as access control lists and rotating IP addresses or with complex solutions like Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) protocol tunnels and virtual private networks (VPNs). In 2018 Cloudflare introduced the Argo Tunnel as a solution to alleviate this problem. Individuals can create a secure and private connection between their source server and Cloudflare, even without a publicly accessible IP address and port.
Cloudflare Tunnel [1] allows you to access your servers and applications securely from anywhere in the world. It creates an encrypted tunnel between your secured server and Cloudflare's network, allowing you to bypass firewalls, geolocation constraints, and all other network restrictions (Figure 1). You can access your server from anywhere without worrying about security threats or network limitations. The Cloudflare architecture removes the public entry point; thus, attackers find no vulnerable places with a potential for attack.
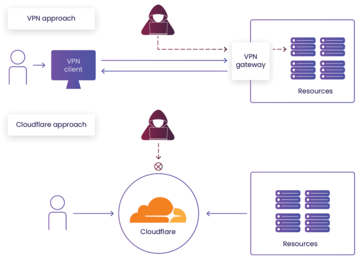 Figure 1: A VPN keeps an open entry to resources at the VPN appliance gate. Cloudflare Tunnel initiates a connection to Cloudflare Access, which then
Figure 1: A VPN keeps an open entry to resources at the VPN appliance gate. Cloudflare Tunnel initiates a connection to Cloudflare Access, which thenBuy this article as PDF
(incl. VAT)



